Nepal’s construction sector is at the heart of national development, with major infrastructure projects underway to strengthen connectivity, boost energy security, and enhance urban living standards. From highways slicing through the Himalayas to hydropower plants lighting up rural villages, here’s a look at key infrastructure construction updates from across Nepal in April 2025.
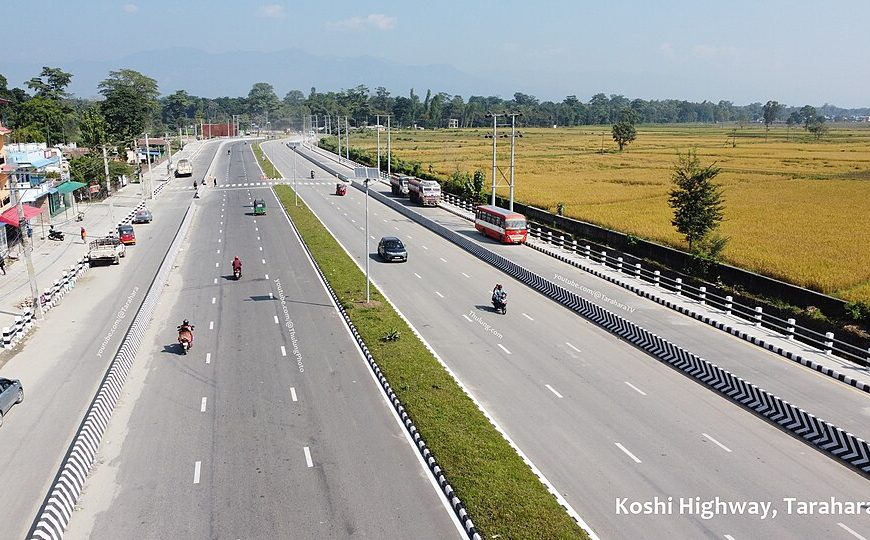
1. Major Road Construction Projects Gaining Momentum
Road construction remains a top priority in Nepal’s development agenda. Key projects currently progressing include:
a. Muglin–Pokhara Highway Upgrade
- Scope: 81 km road being widened into four lanes
- Progress: Over 50% complete
- Objective: Reduce travel time between Kathmandu and the tourist hub Pokhara
- Impact: Boosts tourism, trade, and disaster response access
b. Mid-Hill Highway (Pushpalal Highway)
- Connecting east to west through hilly regions
- Sections in Rolpa, Rukum, and Baglung are under active construction
- Aims to unlock economic potential of mid-hill towns
2. Bridge Construction for River Crossings
Bridges play a crucial role in Nepal’s diverse terrain. As of April 2025, over 150 bridge projects are in various stages of construction.
Notable Projects:
- Koshi River Bridge (Sunsari–Saptari): A multi-span steel bridge being constructed to withstand heavy monsoon flooding
- Bridge over Karnali River in Rajapur: A vital link for western provinces, built using earthquake-resilient design
- Upgradation of old Bailey bridges to permanent RCC and steel structures in Province 1 and 2
Insight: The Department of Roads has set a target to complete 500 bridges by mid-2026 under the Strategic Road Network (SRN) initiative.
3. Hydropower Construction Surges Nationwide
Hydropower development is central to Nepal’s energy independence and export strategy. Key hydropower construction updates include:
a. Upper Tamakoshi Hydropower Project – Final Works
- Capacity: 456 MW
- Status: Almost fully operational
- Location: Dolakha District
- Significance: Nepal’s largest domestic power project to date
b. Arun III Project (900 MW)
- Funded by: India’s SJVN Ltd.
- Construction of dam, tunnels, and transmission lines ongoing
- Expected Completion: 2026
c. Upper Trishuli-1 (216 MW)
- Backed by international financing including IFC and K-Exim
- Construction includes access roads, diversion tunnels, and power stations
Growth: Nepal aims to produce 5,000 MW of hydropower by 2030, with many medium- and small-scale projects in pipeline.
4. Public Infrastructure: Hospitals, Schools, and Government Buildings
Several public infrastructure projects are under active construction to serve growing urban and rural populations.
Ongoing Highlights:
- National Trauma Center Extension – Kathmandu: Expanding surgical and emergency capacity
- New Provincial Hospital – Surkhet: Multi-story facility with modern earthquake-resistant design
- Model Schools in Rural Districts: Built with prefab technology and green sanitation systems
- Administrative Complex in Itahari: Government offices being relocated to a new energy-efficient building
Sustainability: Most new buildings are being constructed with a focus on solar power, rainwater harvesting, and seismic resilience.
5. Urban Infrastructure & Smart City Elements
Urban infrastructure is being modernized through municipal-level investments in transport and public utilities.
Key Developments:
- Integrated Bus Terminals in Pokhara and Dharan
- Underground cable and drainage system in Lalitpur
- Smart water management system under trial in Bharatpur
These projects are often supported by the Asian Development Bank (ADB) and World Bank, along with municipal governments.
Conclusion
Infrastructure construction in Nepal is not just about building roads and power stations—it’s about building the future. These projects create thousands of jobs, improve accessibility, boost trade, and provide essential services to millions.
As we move further into 2025, Nepal’s infrastructure landscape is being reshaped by engineering ambition, international partnerships, and the growing demand for sustainable and resilient construction practices.