The traditional approach of building and developing infrastructure is crucial for the social and economic progress of any nation. It is widely accepted that a country’s growth is based on various factors, including infrastructure development. When we hear about the importance of infrastructure, we naturally start to wonder about the state of our own country’s infrastructure and what steps are needed to transform it.
Infrastructure Development in Nepal
Infrastructure is a vital component of Nepal’s economic and social progress. As a landlocked country with diverse and challenging terrain, Nepal relies heavily on well-developed infrastructure to overcome geographical obstacles, connect different regions, and drive economic activities. Here are some key reasons why infrastructure development is essential for Nepal:
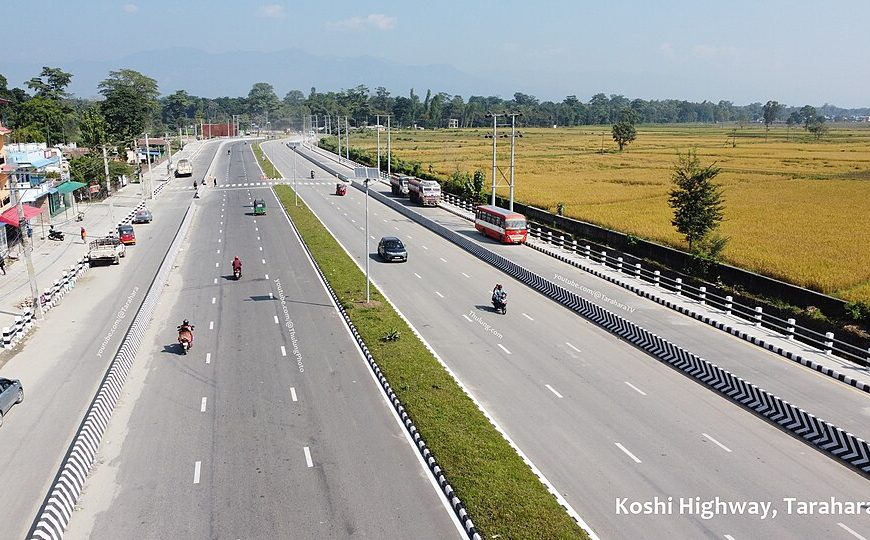
Connectivity and Trade Infrastructure such as roads, railways, and ports enables the efficient movement of goods, services, and people. Improved connectivity within Nepal and with neighboring countries expands trade opportunities and promotes economic integration. It boosts economic growth and job creation by facilitating the transportation of agricultural produce, industrial goods, and tourism.
Regional Development It is crucial to develop infrastructure in rural and remote areas to include them in the national development process. Well-connected roads, bridges, and communication networks can deliver essential services like healthcare, education, and clean water to these communities, improving living standards and reducing regional disparities. It also encourages migration away from overcrowded urban areas, leading to more balanced growth across the country.
Energy & Power Supply Ensuring adequate energy infrastructure, such as hydropower projects and transmission lines, is vital for Nepal’s energy security and economic prosperity. Nepal has abundant water resources, and harnessing hydropower can provide clean, affordable electricity for domestic use and export. Improved electricity supply also promotes industrial growth and job creation while reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Tourism and Hospitality Nepal’s natural beauty, cultural heritage, and potential for adventure tourism attract a large number of tourists. Developing infrastructure such as airports, hotels, and tourist facilities enhances the capacity and competitiveness of the tourism industry. It generates foreign currency earnings, creates job opportunities, and boosts local economies.
Disaster Resilience Nepal is prone to natural disasters like earthquakes, landslides, and floods. Investing in resilient infrastructure, including sturdy buildings, early warning systems, and disaster management facilities, helps mitigate risks and ensures quick recovery after disasters. Building infrastructure that can withstand seismic activities is crucial for the safety of the population and the sustainability of economic activities.
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Infrastructure A well-developed ICT infrastructure, including broadband connections and digital networks, promotes innovation, e-commerce, and knowledge exchange. It improves access to information, education, and healthcare, especially in rural areas. Investing in digital infrastructure also helps the IT sector thrive by creating jobs and increasing economic output.
Social Development and Well-being Social well-being is directly influenced by infrastructure development. Accessible transportation systems reduce travel times, increase mobility, and improve access to essential services such as healthcare and education. Improved infrastructure for water supply, sanitation, and waste management benefits public health and hygiene. A better living environment is promoted through improved urban infrastructure, including housing, public spaces, and recreational facilities.
The Rise of Infrastructure Development in Nepal In recent years, Nepal has made significant progress in infrastructure development, focusing on improving transportation, electricity, and urban growth. Several major construction projects have been undertaken to strengthen the country’s infrastructure. Here are a few notable examples:
Highways and Roads
- Kathmandu-Terai Fast Track: This ambitious project aims to connect the capital city of Kathmandu with the southern plains via a 76-kilometer motorway. It will greatly reduce travel time and enhance connectivity.
- Mid-Hill Highway: This 1,700-kilometer project seeks to connect various regions of Nepal, improving transportation and accessibility to remote areas.
- East-West Highway: This 1,024-kilometer critical highway project connects Nepal’s eastern and western provinces, expected to boost transportation and accessibility in remote regions.
Airports
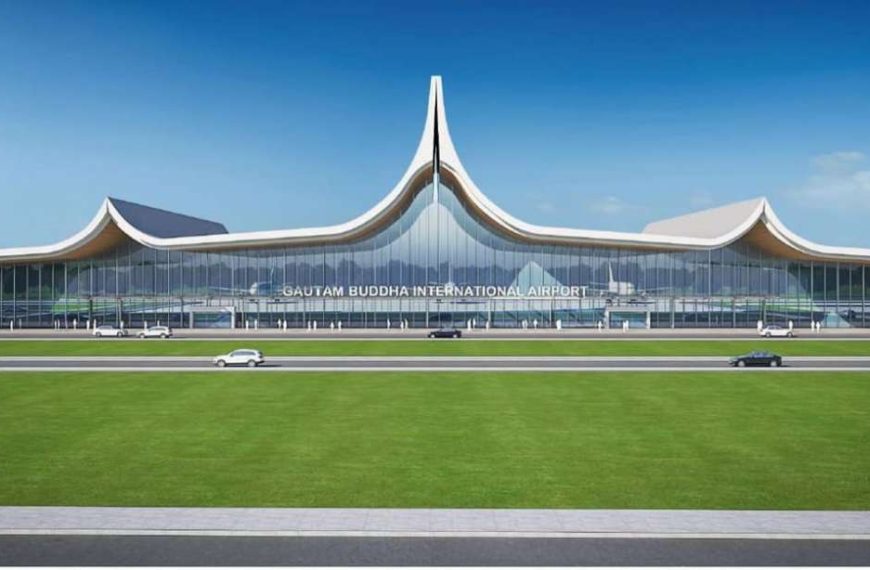
- Gautam Buddha International Airport: Currently under development near Bhairahawa, this airport is expected to be one of Nepal’s largest. It will serve as an international gateway to Lumbini, a UNESCO World Heritage site and the birthplace of Lord Buddha.
- Nijgadh International Airport: Located in Bara district, this mega airport project aims to meet Nepal’s growing air travel demand. Once completed, it will accommodate millions of travelers annually.
Hydroelectric Projects
- Upper Tamakoshi Hydroelectric Project: This significant hydropower project in the Dolakha region has a projected capacity of 456 MW. It will contribute to Nepal’s energy needs and reduce reliance on imported electricity.
- Upper Karnali Hydroelectric Project: Currently under construction in the Karnali River basin, this project has a planned capacity of 900 MW and is expected to significantly boost Nepal’s hydropower output.
Urban Development
- Kathmandu Valley Road Expansion: The government has been working on expanding and improving roads in the Kathmandu Valley to alleviate traffic congestion and enhance connectivity within the city.
- Smart City Initiatives: The concept of smart cities is rapidly gaining traction in Nepal to improve urban infrastructure and services. Projects focused on smart transportation, waste management, and sustainable development are being explored.
Conclusion
These infrastructure development projects in Nepal aim to enhance connectivity, promote economic growth, and improve the overall quality of life for Nepalese citizens. The government is committed to supporting sustainable development and ensuring the successful completion of these projects in collaboration with various development partners.