Nepal’s diverse topography and dispersed rural communities present unique challenges for infrastructure development. Recognizing the pivotal role of rural infrastructure in fostering inclusive growth, the government, in collaboration with international partners, has initiated several programs aimed at enhancing connectivity, access to services, and economic opportunities in remote areas.
Key Initiatives and Achievements
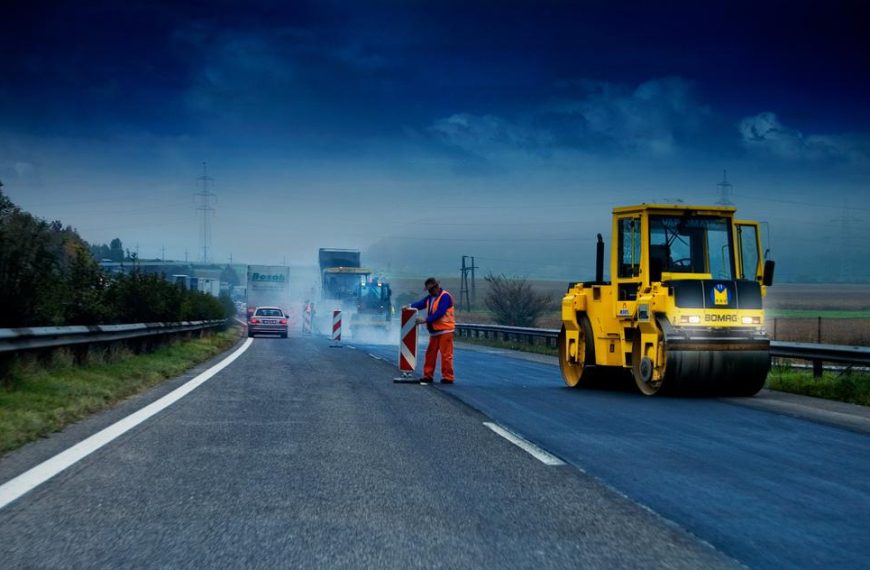
One significant effort is the Decentralized Rural Infrastructure and Livelihood Project, which aims to reduce rural poverty in 18 poor and remote hill and mountain districts by widening access to economic and social services . Similarly, the Rural Access Improvement and Decentralization Project focuses on improving existing rural roads, constructing trail bridges, and supporting the capacity of local governments .
In the aftermath of the 2015 earthquake, Nepal undertook extensive reconstruction efforts. Approximately 95% of houses damaged in rural areas have been rebuilt, with public infrastructure, especially schools, upgraded to meet new safety standards .
Impact on Communities
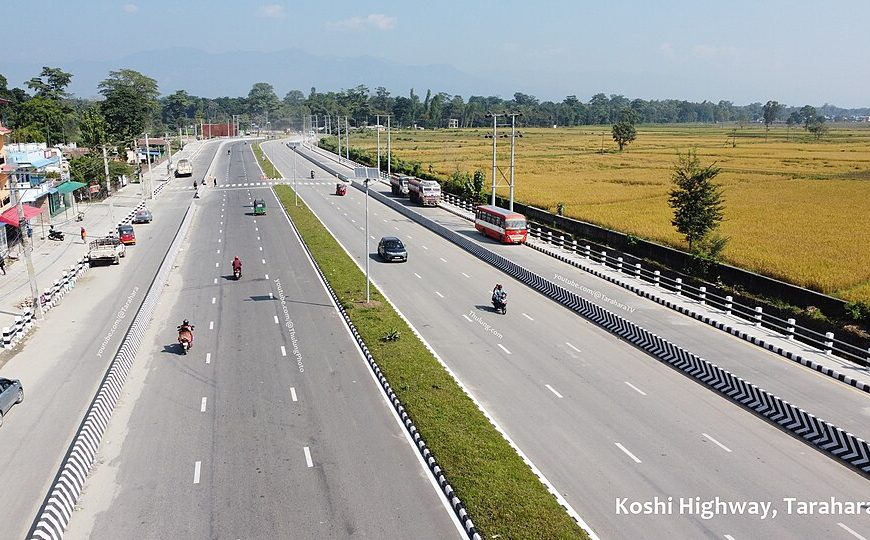
Improved infrastructure has revitalized rural economies by facilitating access to markets, education, and healthcare. Farmers can now transport their produce more efficiently, leading to increased incomes. School enrollment among disadvantaged groups has risen, and healthcare facilities have become more accessible, particularly in mountainous regions .
Challenges and the Way Forward
Despite these advancements, challenges persist, including funding constraints, maintenance of infrastructure, and ensuring equitable access across all regions. To address these issues, continued investment, capacity building at the local level, and inclusive planning processes are essential.
By strengthening rural infrastructure, Nepal can promote inclusive growth, reduce poverty, and enhance the resilience of its rural communities.